Probability of Detection (POD) in Pharma Visual Inspection: A Practical Knapp Methodology Guide
Introduction: Why POD Is the Metric Regulators Actually Care About
Visual inspection in pharmaceutical manufacturing has changed permanently.
It is no longer acceptable to say:
- “Inspectors are trained”
- “We follow SOPs”
- “Defects are visually checked”
Regulators today ask one fundamental question:
Can you prove that your inspectors and systems consistently detect defects?
That proof comes from Probability of Detection (POD) in pharma visual inspection.
POD transforms visual inspection from a subjective human activity into a measurable, defendable quality process. And the most widely accepted way to establish POD is through Knapp methodology and Knapp kits.
This guide explains:
- What POD really means in pharma
- Why POD is central to USP <790> & <1790>
- How Knapp methodology enables POD studies
- How to implement POD practically (not theoretically)
- How POD strengthens audit readiness
If you are responsible for QA, QC, validation, or inspection compliance, this guide is written for you.
1. What Is Probability of Detection (POD) in Pharma Visual Inspection?
Probability of Detection (POD) in pharma visual inspection is a statistical measure that answers:
Out of 100 inspection opportunities, how often is a known defect detected under defined conditions?
It is expressed as a percentage.
Simple Example
- A vial containing a known glass particle is inspected 40 times
- The particle is detected 32 times
- POD = 80%
This number tells regulators far more than subjective statements ever could.
2. Why POD Is Critical for Patient Safety
In sterile and injectable products, missing a defect = patient risk.
Regulators understand that:
- Not every defect is visible 100% of the time
- Human detection varies
- Lighting, fatigue, and defect type affect outcomes
That’s why they expect manufacturers to:
- Identify which defects must be detected
- Prove detection capability statistically
- Design inspection processes around realistic limits
Probability of Detection (POD) in pharma visual inspection is how this risk is controlled.
3. Regulatory Drivers Behind POD Requirements
USP <790> – Visible Particulates
USP <790> requires:
- 100% visual inspection
- Qualified inspectors
- Controlled inspection conditions
But it implicitly expects proof that inspectors can actually detect particles.
USP <1790> – Visual Inspection of Injections
USP <1790> makes POD unavoidable.
It introduces:
- Risk-based inspection
- Statistical evaluation
- Performance monitoring of inspection systems
It explicitly encourages POD-based approaches.
EU GMP Annex 1 (2023 Revision)
Annex 1 requires:
- Qualification of inspection processes
- Justification of defect detection capability
- Ongoing monitoring
All of these point directly to Probability of Detection (POD) in pharma visual inspection.
4. The Knapp Methodology: The Foundation of POD Studies
The Knapp methodology, developed by Dr. John E. Knapp, was the first structured approach to apply POD concepts to pharmaceutical visual inspection.
Core Principles of Knapp Methodology
- Use realistic, known defects
- Inspect each unit multiple times
- Involve multiple inspectors
- Calculate detection probability
- Classify defects based on POD
This methodology is operationalized using Knapp kits for visual inspection.
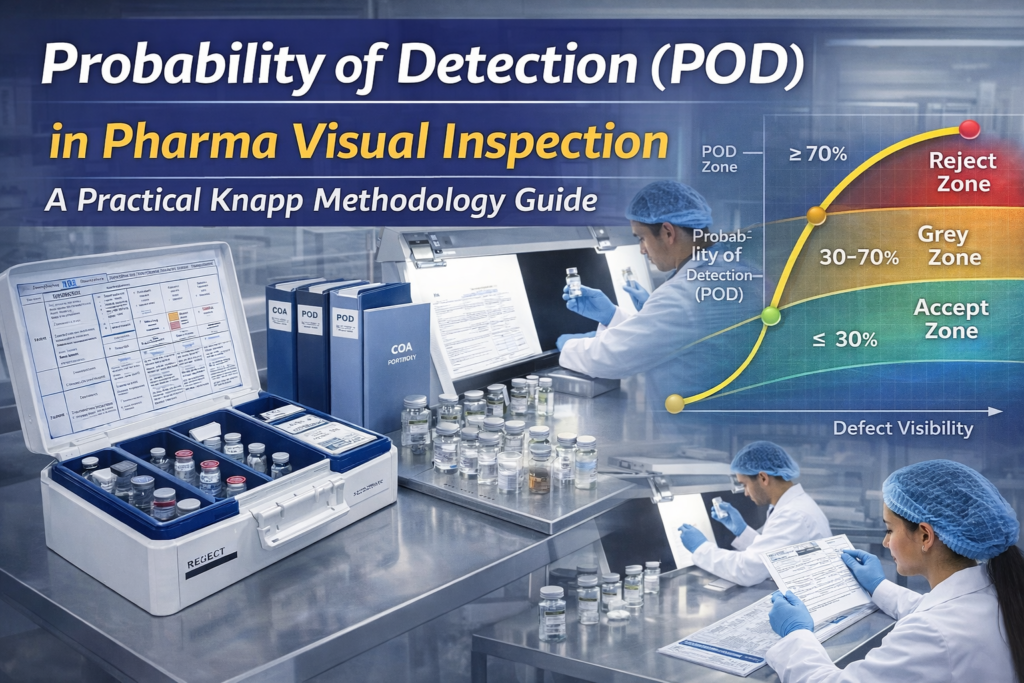
5. POD Zones Defined in Knapp Methodology
Knapp methodology divides defects into three zones:
Reject Zone
- POD ≥ 70%
- Defects that must be consistently detected
- Typically critical patient safety risks
Grey Zone
- POD 30–70%
- Detection is variable
- Use must be justified and controlled
Accept Zone
- POD ≤ 30%
- Not expected to be reliably detected
- Usually cosmetic or low-risk
This classification is central to Probability of Detection (POD) in pharma visual inspection.
6. What Are Knapp Kits and Why They Are Essential for POD?
Knapp kits are standardized visual inspection qualification kits containing containers with known defects.
They are used to:
- Establish POD values
- Qualify inspectors
- Validate inspection systems
- Support audits
Typical Knapp Kit Contents
- Glass particles (various micron ranges)
- Metal particles
- Fibers (black, white, hair)
- Black & white particles
- Vials, ampoules, syringes
- Certification & documentation
Without Knapp kits, POD studies lack credibility.
7. How POD Studies Are Performed Using Knapp Kits
Step 1: Define Inspection Conditions
- Lighting (2,000–3,750 lux)
- Background (black & white)
- Inspection time per unit
- Inspector posture and technique
Step 2: Inspect Each Knapp Unit Multiple Times
- Typically 30–50 inspections per unit
- Conducted across multiple sessions
- Performed by multiple inspectors
Step 3: Record Detection Results
- Detected / Not detected
- Logged systematically
- No feedback during testing
Step 4: Calculate POD
POD=Number of DetectionsNumber of Inspections×100POD = \frac{\text{Number of Detections}}{\text{Number of Inspections}} \times 100POD=Number of InspectionsNumber of Detections×100
This data forms the backbone of Probability of Detection (POD) in pharma visual inspection programs.
8. Manual Visual Inspection: POD Application
For manual inspection, POD is used to:
- Qualify new inspectors
- Requalify experienced inspectors
- Compare inspector performance
- Identify training needs
Inspectors must demonstrate acceptable POD values for reject-zone defects.
9. Automated Visual Inspection (AVI): POD Still Applies
POD is not limited to humans.
Knapp kits are also used to:
- Challenge automated inspection machines
- Compare machine vs human detection
- Validate defect detection thresholds
- Support IQ/OQ/PQ
This makes Probability of Detection (POD) in pharma visual inspection a lifecycle concept.
10. Common Mistakes in POD Studies (Audit Red Flags)
Avoid these errors:
❌ Using demo or artificial defects
❌ No repeat inspections
❌ No statistical analysis
❌ Mixing training with qualification
❌ No documentation of lighting or conditions
❌ Overuse of grey-zone defects
Auditors don’t fail POD—they fail poorly designed POD studies.
11. How POD Strengthens Audit Readiness
During audits, inspectors often ask:
- How do you qualify visual inspectors?
- How do you justify defect detectability?
- What is your POD for critical defects?
- How do you monitor inspection performance?
With proper POD studies using Knapp kits, answers are:
- Data-backed
- Documented
- Consistent
- Defendable
12. Practical Benefits of POD-Based Visual Inspection
Implementing Probability of Detection (POD) in pharma visual inspection helps you:
- Reduce inspection variability
- Improve inspector confidence
- Shorten training cycles
- Reduce audit observations
- Strengthen patient safety
- Support regulatory submissions
13. Best Practices for Sustainable POD Programs
- Use certified Knapp kits
- Maintain a master defect log
- Schedule periodic requalification
- Trend POD results over time
- Integrate POD into SOPs
- Link POD outcomes to training plans
14. Why Certified Knapp Kits Make the Difference
High-quality Knapp kits offer:
- Certified particle sizes
- Representative defect types
- Full traceability
- Audit-ready documentation
- Long shelf life
- Replacement support
This directly impacts the credibility of POD in pharma visual inspection.
👉 Explore certified Knapp Kits here:
https://confiancapharmazon.com/product/knapp-kit-visual-inspection-kits-particles-particulate-matters/
FAQ: POD & Knapp Methodology
Q1. Is POD mandatory in pharma visual inspection?
Not named explicitly, but regulators clearly expect equivalent statistical justification.
Q2. What POD is acceptable for reject defects?
Typically ≥70%, but justification must be risk-based.
Q3. How often should POD studies be repeated?
Usually annually or after significant changes.
Q4. Can POD be improved with training?
Yes—POD trends often guide targeted retraining.
Conclusion: POD Is the Language Regulators Understand
Visual inspection without POD is opinion.
Visual inspection with POD is evidence.
By implementing Probability of Detection (POD) in pharma visual inspection using Knapp methodology and certified Knapp kits, manufacturers move from assumption to assurance.
This is no longer optional—it is modern GMP compliance.
Strong CTA
👉 Upgrade your visual inspection program with certified Knapp Kits
Ensure defensible POD studies, inspector qualification, and audit readiness.
🔗 View Knapp Kit Product Page:
https://confiancapharmazon.com/product/knapp-kit-visual-inspection-kits-particles-particulate-matters/
Your trusted partner for pharma skills, systems, and solutions.



